학습할 것
- 산술 연산자와 대입 연산자
- 비트 연산자
- 관계 연산자
- 논리 연산자
- instanceof
- assignment(=) operator
- 화살표(->) 연산자
- 3항 연산자
- 연산자 우선 순위
- (optional) Java 13. switch 연산자
1. 산술 연산자와 대입 연산자
| 연산자 | 사용 예제 | 설명 |
| = | a = 3; | 대입 연산자입니다. |
| + | b = a + 2; | 변수a와 2를 더하여 b에 대입 |
| - | c = b - 2; | 변수b에 2를 뺀 후 c에 대입 |
| * | d = c * 2; | 변수c에 2를 곱한 후 d에 대입 |
| / | e = d / 4; | 변수d에 2를 나눈 몫을 e에 대입 실수의 경우 나눈 값을 대입 |
| % | f = d % 4; | 변수f에 2를 나눈 나머지를 e에 대입 실수의 경우 나머지를 대입 |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 18 19 20 |
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 3;
int b = a + 2;
int c = b - 2;
int d = c * 2;
int e = d / 4;
int f = d % 4;
double f1 = d % 4.0; double f1 = d % 4.0; System.out.println("a : "+a);
System.out.println("b : "+b);
System.out.println("c : "+c);
System.out.println("d : "+d);
System.out.println("e : "+e);
System.out.println("f : "+f);
System.out.println("f1: "+f1); System.out.println("f2: "+f2); }
}
|

2. 비트 연산자
| 연산자 | 사용 예제 | 설명 |
| ~ | a = ~b | b의 모든 비트들을 반전시켜 a에 대입 |
| & | a = b & 3 | b의 각 비트들과 3의 비트를 곱하여 대입 |
| | | a = b | 3 | b의 각 비트들과 3의 비트를 더하여 대입 |
| ^ | a = b ^ 3 | b의 각 비트들과 3의 비트를 xor연산 |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a;
int b = 10; // 1010
a = ~b;
System.out.println(a+":"+Integer.toBinaryString(a));
a= b & 3; // 3 = 0011
System.out.println(a+":"+Integer.toBinaryString(a));
a = b | 3;
System.out.println(a+":"+Integer.toBinaryString(a));
a = b ^ 3;
System.out.println(a+":"+Integer.toBinaryString(a));
}
}
|

첫번째는 1010의 모든 비트를 반전 시킵니다. 다만 출력 값에서는 Integer즉 32bit를 전부 표현했기에 나왔지만 마지막 4개의 비트를 보면 0101로 반전된 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 나머지는 and, or, xor연산을 순서대로 한 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
3. 관계 연산자
| 연산자 | 사용 예제 | 설명 |
| > | a > b | a가 b보다 큰가? |
| >= | a <= b | a가 b보다 크거나 같은가? |
| < | a < b | a가 b보다 작은가? |
| <= | a <= b | a가 b보다 작거나 같은가? |
| == | a == b | a와 b가 같은가? |
| != | a != b | a와 b가 같지 않은가? |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 3;
int b = 3;
String s1 = "HI";
String s2 = "HI";
String s3 = new String("HI");
String s4 = new String("HI");
System.out.println("a<b ? "+(a<b));
System.out.println("a<=b ? "+(a<=b));
System.out.println("a>b ? "+(a>b));
System.out.println("a>=b ? "+(a>=b));
System.out.println("s1==s2 ? "+(s1 == s2));
System.out.println("s3==s4 ? "+(s3 == s4));
System.out.println("s1==s3 ? "+(s1 == s3));
}
}
|
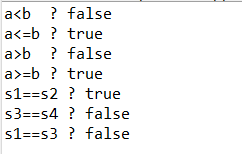
문자열의 비교는 저번 포스트 에서 다뤘듯이 ==는 주소 값을 비교하게 됩니다. s1과 s2는 모두 constant pool에서 같은 값을 가져오기에 같지만 s3과s4는 각각의 객체를 새로 만들어서 Heap에 저장 했기에 다른 주소를 가지고 있어서 false가 나온 것을 볼 수있습니다.
4. 논리 연산자
| 연산자 | 사용 예제 | 설명 |
| ! | !bool | boolean에 대해 반전 시킵니다. |
| && | (b>=5) && (b<=7) | b가 5~7사이에 있는가? |
| || | (b<5) || (b>7) | b가 5보다 작거나 7보다 큰가? |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean bool = false;
int a = 3;
int b = 6;
System.out.println(!bool);
System.out.println("5<=b<=7: "+((b>=5) && (b <= 7)));
System.out.println("b<5, b>7: "+((b<5) || (b > 7)));
}
}
|

5. instanceof
- 객체가 타입을 확인하는데 사용
- 인스턴스가 특정 클래스의 객체인지 확인
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Example ex = new Example();
Example uc = new SubClass();
SubClass sc = new SubClass();
SubClass dc = (SubClass)uc;
System.out.println("ex(Ex): " +(ex instanceof Example)+", ex(Sub): "+(ex instanceof SubClass));
System.out.println("uc(Ex): " +(uc instanceof Example)+", uc(Sub): "+(uc instanceof SubClass));
System.out.println("sc(Ex): " +(sc instanceof Example)+", sc(Sub): "+(sc instanceof SubClass));
System.out.println("dc(Ex): " +(dc instanceof Example)+", dc(Sub): "+(uc instanceof SubClass));
}
}
|

6. assignment(=) operator
| 연산자 | 사용 예제 | 설명 |
| (연산자)= | a (연산자)= b; | a와 b를 연산자를 통해 연산한다. |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 5;
int b;
a += 1;
System.out.println(a);
a -= 1;
System.out.println(a);
a *= 2;
System.out.println(a);
a /= 2;
System.out.println(a);
a %= 2;
System.out.println(a);
a &= 3;
System.out.println(a);
a |= 3;
System.out.println(a);
a ^= 1;
System.out.println(a);
a <<=3;
System.out.println(a+":"+ Integer.toBinaryString(a));
a >>=3;
System.out.println(a+":"+Integer.toBinaryString(a));
a = ~a;
b = a;
System.out.println(a+" :"+Integer.toBinaryString(a));
a >>>=1;
System.out.println(a+":"+Integer.toBinaryString(a));
b >>=1;
System.out.println(b+" :"+Integer.toBinaryString(b));
}
}
|
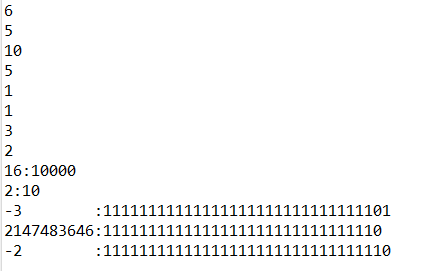
>>>의 경우 부호에 상관없이 우로 시프트를 시키기 때문에 좌측 끝은 항상 0이 들어옵니다. >>는 부호를 유지한 채 우로 시프트 하므로 좌측 끝에 부호에 맞에 음수면 1, 양수면 0이 들어오게 됩니다.
7. 화살표(->) 연산자
- 람다 표현식 문법 중 일부
- 불필요한 코드 줄이고 가독성 향상을 위해 도입
(이후 추가적으로 업로드 하겠습니다.)
8. 3항 연산자
- 다른 연산자와 다른 구조를 가짐
- 조건식 ? 참 반환 : 거짓 반환
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 6;
int b = 7;
System.out.println("더 큰 수 : "+(a>b?a : b));
}
}
|
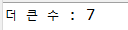
9. 연산자 우선 순위
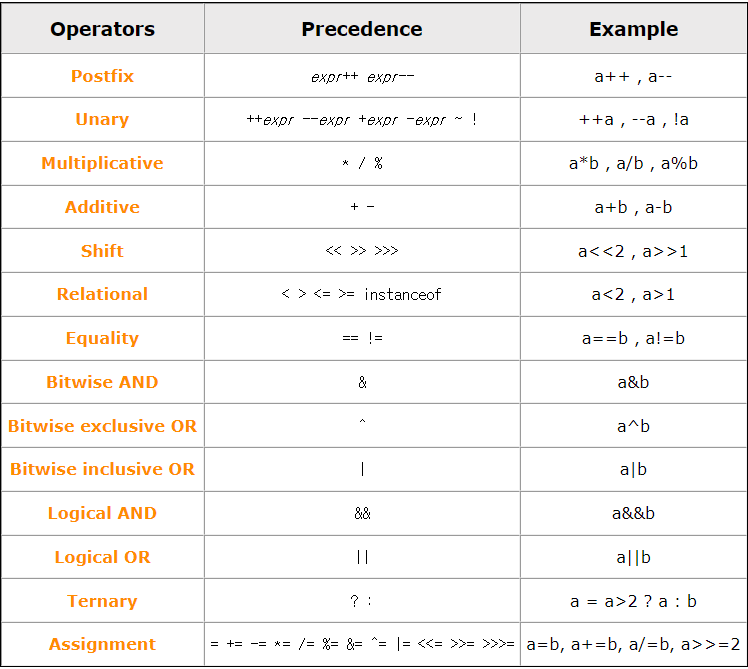
위에 있을 수록 높은 우선순위를 가지고 있습니다.
10. (optional) Java 13. switch 연산자
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 6;
switch(score) {
case 5:
System.out.println("C");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("B");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("A");
break;
default:
System.out.println("F");
}
}
}
|

score에 대한 학점을 나타낸 것입니다. 만약 더욱 세분화 되었을 때 break;를 안쓰게 되거나 좀 더 코드를 줄일 수 있도록 switch expression이 java14에 추가되었습니다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 3;
char grade = switch(score) { //방법 1
case 5:
yield 'C';
case 6:
yield 'B';
case 7:
yield 'A';
default:
System.out.println("None");
yield 'F';
};
System.out.println(grade);
score = 5;
System.out.println( //방법 2
switch(score) {
case 5 -> 'C';
case 6 -> 'B';
case 7 -> 'A';
default ->"None";
}
);
score = 7;
switch(score) { //방법 3
case 5->grade='C';
case 6->grade='B';
case 7->grade='A';
default -> {
grade = 'F';
System.out.println("None");
}
}
System.out.println(grade);
}
}
|
State Expression
- 방법 1 : yield를 통해 값을 변수에 반환
- 방법 2 : 바로 print하는 방법
- 방법 3 : switch문 내부에서 변수에 값을 저장 후 실행
'JAVA > 자바스터디' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자바스터디] 5. 클래스 (0) | 2022.01.06 |
|---|---|
| [자바스터디] 4. 선택문, 반복문 (0) | 2022.01.06 |
| [자바스터디] 2. 변수 (0) | 2022.01.02 |
| [자바스터디] 1.1 컴파일과 실행하는 법 (0) | 2021.12.27 |
| [자바스터디] 1. JAVA와 JVM (0) | 2021.12.27 |
![[자바스터디] 3. 연산자](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FCnqmp%2FbtrpGzJ2Pj7%2FKINGvy79f8lfurtF9s8LS1%2Fimg.png)